JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
UK New Grading System Simplified 9-1
UK New Grading System Simplified Were you the only one among your classmates who obsess over your grades? You should be aware of how various grading systems are in other nations and can also vary from institution to university within the same nation, even though we understand your worries and fear. The UK is a well-liked study abroad destination for students from all over the world due to its prominent colleges, high-quality education, and guarantee of a high standard of grades to build a benchmark globally. For your benefit as you proceed through your study in the UK, we will explain the UK grading system in this blog.
In the UK, students’ academic achievement is assessed using a numerical or alphabetical scale in schools, colleges, and universities. The Scottish grading system is distinct from all three, whereas the UK grading system is uniform throughout England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. The thoughtfully created grading system takes into account elements outside academic performance, like a student’s involvement in extracurricular activities. Keep in mind that if you want to study in the UK, you must be familiar with all aspects of doing so including applying for a UK visa; for more information, see the UK student visa.
Understanding the UK Grading System
Did you realize that the UK has a distinct grading and educational system?The basic scale used in the UK’s grading system is 1 to 10, with 10 representing the highest grade that may be given. These university grades also have a percentage equivalent, with 1 denoting a valid answer of 0% to 5%. 2 indicates a 5–15% correct answer. One of the reasons British higher education is so highly regarded internationally is due to this. Furthermore, the UK Grading system or a variant of it has been adopted by numerous nations. Understanding the grading structure at the university you wish to attend is crucial when planning to study abroad.You’ll be able to convert your grades this way and determine how they compare to the standards. Nevertheless, don’t worry! We have your back. Here is all the information you require on the UK Grading System.
What are GCSE?
General Certificate of Secondary Education is what this term refers for. These are the credentials that fifteen- and sixteen-year-olds in the UK attained after completing Year 11 of school. A standardized framework for evaluation in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland is provided through GCSEs. Scottish Qualifications are pursued in schools in Scotland. Over the course of two years, certificates and chosen subjects are studied and evaluated through final exams or homework.
While there are several GCSE options that students can pick from, some subjects must be taken. These are referred to as basic subjects and comprise
- Maths
- English Literature
- English Language
- Science (in varying forms)
GCSE syllabuses are set, examinations administered, and certificates awarded by five primary examination boards:
- AQA (Assessment and Qualifications Alliance)
- CCEA (Council for the Curriculum Examinations and Assessment)
- Edexcel
- OCR ( Oxford, Cambridge and RSA)
- WJEC ( The Welsh Joint Education Committee)
These are overseen by regulatory authorities to ensure parity between schools using a different exam board.
How does the 9-1 GCSE grading system work?
In England, a new GCSE curriculum was established along with the 9-1 grading system. Currently, a 9 is the highest grade and a 1 is the lowest. The letter U, which denotes “ungraded,” does not change. The old letter one does not exactly match the numerical scale. The essential grades on the new scale will align with those on the current A* to G range. The percentage of pupils who earn a grade of 1 or above will be about the same as the percentage who do so now. Ancient languages (classical Greek and Latin), art and design, biology, chemistry, citizenship studies, combined science (double award), history, and geography are only a few of the subjects that utilise the UK grading system.
Undergraduate Grading System, UK
The UK grading system is quite particular in how it assigns grades, implying that not all students who achieved an A are in the same class as you. The many components necessary for an individual’s entire growth are taken into consideration when evaluating a student’s overall performance in view. Although narrowing it down to the grades, the Undergraduate grading system, UK is split into three major categories, which are further explained as follows:
UK Undergraduate Degree Requirements

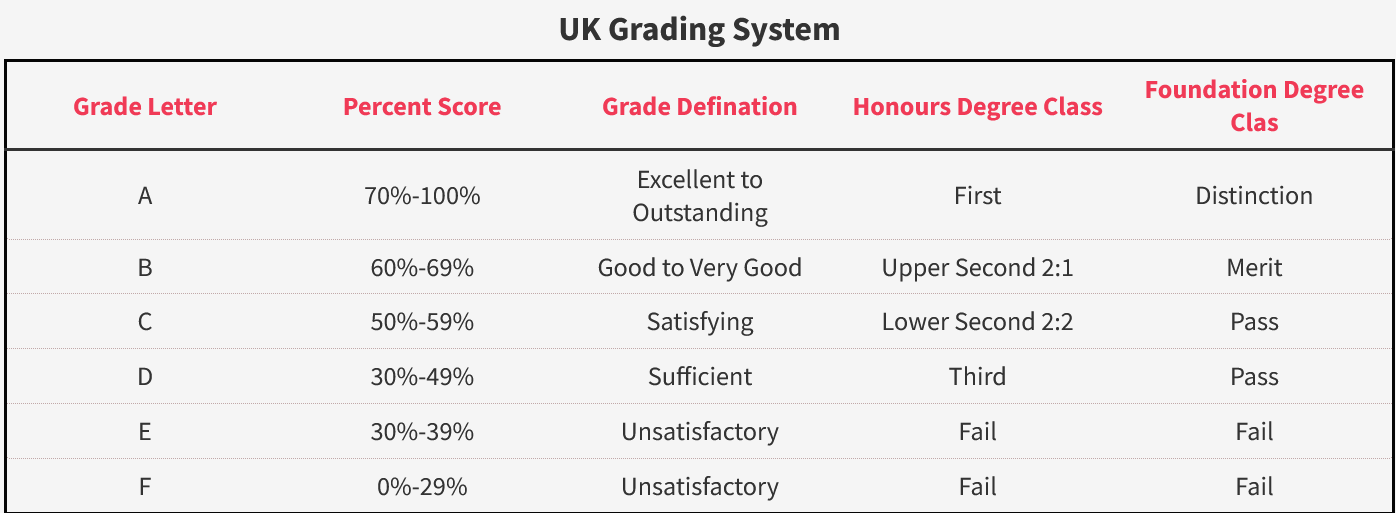
First Class Degree
As per the UK undergraduate grading system, a First Class Degree is the highest you can score during the undergraduate degree and requires students to have a total score greater than 70%. A first-class degree is highly valued in the UK grading system since it suggests that the student thoroughly understands the subject’s material and content. Your prowess in a particular field is crucial to your career, especially your course of interest. A first-class degree with a distinction grade is also known as the First and is considered the most outstanding achievement in the undergraduate course.
Second Class Degree
According to the UK undergraduate grading system, the second-class degree is further segregated into two categories –
- Upper Second Class degree, named 2:1, represents that the student has scored somewhere between 60-69%. Though, because of the tough competition in the present times, first-class degree holders are captivating the opportunity market. This grading system says that you have performed well but can still work on and strive to develop yourself in numerous ways.
- Lower Second Class Degree, known as 2:2, comes right after the upper second-class degree, which shows that your score ranges around 50%-59% according to the UK grading system. It indicates that you need to put in a lot of effort to improve your knowledge and understanding of the relevant subject because it is slightly below the upper second-class degree.
Third Class Degree
In the UK undergraduate grading system, this is the lowest score an undergraduate candidate can achieve. Students who earn between 40% and 49% receive a third-class degree. Having this degree indicates you have a lot of room to grow, so you should start advancing yourself and your field knowledge. Although we know you’re a champ and that you would be scoring more than this and won’t fall in this category.
There was a Fourth Class Degree in the UK grading system offered by a few universities there, including Oxford. A student grade who narrowly missed earning a Third Class Degree is now granted an ordinary degree marked Pass.
Master’s Grading System UK
The UK Master’s grading system is slightly different compared to the scheme used for undergraduate degrees. If you are planning your Master’s in UK, make sure you understand their process. The Master’s grading system, UK differs from all the countries worldwide. Like the undergraduate degree, postgraduate degrees offer grades using four levels:

Master’s UK Degree Requirements
Here are some of the most important UK master’s grading system requirements :
- Distinction: When students receive a distinction, they are considered to have achieved a master’s degree score of at least 70%.
- Merit: Students who receive grades from 60% to 69% are granted a merit grade.
- Pass: Passing is defined as having an overall grade between 50% and 59%.
- Borderline Pass/ Fail: As the name implies, this category includes students who narrowly avoid failing or passing but receive a score between 40% to 49%.
The Master’s grading system, UK also depends upon the type of Master’s course you are pursuing. The three most popular categories of Master’s in the UK are as follows:
Integrated Master’s Degree
This is an integrated degree that combines both a graduate and postgraduate degree. It generally consists of three years of undergraduate and one-year postgraduate study. This means that when you apply for an undergraduate degree, you are already aware of the Master’s you will pursue post that. This is a more specialised qualification and a commitment for four years. The grade is given as follows:
- Distinction: Minimum 70%
- Merit: Between 60% to 69%
- Pass: Between 50% to 59%
- Borderline Pass/ Fail: Between 40% to 49%
Taught Master’s Degree
The main components of this Master’s programme include lectures, seminars, and tutorials. The public speaking requirements of this course may seem intimidating at first, but we assure you that you will become more confident with practice! These courses usually include research and dissertation elements, making it essential for you to work around the year.
The grades provided in a taught Master’s degree typically go as fail, pass, merit, and distinction and usually have the same percentage and markings as Integrated Master’s Degree. However, a taught master’s degree often calls for 180 credits of study, which includes modules, dissertations, assignments, and research. The number of credits you get for each module varies from 10 to 30, depending on the quantity and quality of the work.
Master’s Degree Research (MRes)
Considering pursuing a Master’s in research? The Credit Accumulation and Transfer Scheme, similar to the Taught Master’s Degree, is the standard credit structure for MRes. The course’s research component might result in 160 credits, 20 of which would be given for training. The overall course may include one single research and dissertation or multiple projects at the same time. The grading is usually done as Pass or fail, but usually, some universities also offer distinction as a classification for students who score higher than 70%.
Want more in-depth information on the degrees in the UK? This Types of Degrees in UK guide will answer every question you have regarding the degrees in UK.
The Difference Between the US vs UK Grading Systems
The main difference is that exams and things like your dissertation or work you produce for the final semester of your course are given a lot more weight than GPA, which is an amalgamation of your marks over the academic year. The United Kingdom uses letter grades, but not in the same way that the United States does. In the UK, an A is anything above 70%, rather than each letter representing 10%. And each letter after that represents a 10% reduction. A failing grade is also unique. For example, a score of less than 59% in the United Kingdom is sufficient to obtain an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. This, however, is not possible in the United States.
UK Grading System and ETCS grades
The UK grading system used in higher education institutions is based on a scale that ranges from A* to E for undergraduate Degrees and A to D for postgraduate degrees. The A* to E scale is further divided into subgrades such as A*, A, B, C, D and E, where A* is the highest grade, and E is the lowest passing grade.
The European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) grades are a system used in Europe to facilitate academic recognition to study period qualifications. The ECTS grading scale ranges from A to E, with A being the highest grade and E being the lowest passing grade.
It’s important to note that while the UK and ECTS grading systems may have similar grades, the criteria for earning each can differ from institution to institution and from country to country. Therefore students need to understand the specific grading criteria for their program and university.
UCAS Points
UCAS Points which are also known as UCAS Tariff Points are an adjacent way to measure and compare the achievements of a student studying in the UK. These points are basically assessed by the university to ensure the suitability of a student for their chosen course. These points assign a numerical value to the different qualifications and grades making it convenient for the universities to make a fair and uniform comparison among applicants.
It directly impacts the UK grading system as it provides a common metric to compare diverse qualifications. As the UCAS points assigns a number to different qualifications and grades of the students, universities and colleges in the UK usually set their entry and admission parameter based on the same factor.
For instance, a grade B might only be worth 100 UCAS points, but an A might be worth 120. Institutions can establish uniform standards and make unbiased judgements about which candidates fit their requirements by establishing the number of UCAS points necessary for admission. Wish to know more about UCAS? Here is our comprehensive to help you understand what UCAS is all about!
Refference
https://amberstudent.com/blog/post/uk-grading-system-simplified
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE

Be the first to comment