JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
How to check SAICA ITC AND APC Exam Results – www.saica.co.za 2024 /2025
How to check SAICA ITC AND APC Exam Results – www.saica.co.za 2024 /2025 Have you looking for South African Institute of Chartered Accountants (SAICA) ITC and APC Exams Results? This Article is Accuracy it Contain Guide and Steps How to Check SAICA ITC Exams Results and SAICA APC Exams Results.
SAICA is at the forefront of developing, influencing and leading the highest standards of ethics, education and professional excellence in the delivery of quality accountancy skills. This is achieved by safeguarding the professional standards of the designations on offer; advancing and maintaining the relevance of the profession; and by regulating the members’ and associates’ professional conduct against the SAICA Code.
Our history
Four decades and more of SAICA
Since the founding of the South African Institute of Chartered Accountants (SAICA) in 1980, much has transpired for the profession worldwide. SAICA was already functioning and influencing major changes to the profession in the mid-1990s when a united South Africa emerged under Nelson Mandela as President. Yet, it also becomes clear that a summary of SAICA’s achievements cannot reflect the environment in which it operates without also referring briefly to its earlier roots.
The local history of the profession in South Africa may have started when Frederick Verburgh landed at the Cape at the same time as Jan van Riebeeck (1652) to become bookkeeper-in-residence to the Dutch East India Company (VOC).
Through the decades and centuries since then, the events that led to creating SAICA followed circuitous routes through the discovery of diamonds and gold that supercharged the local economy in the late 19th century, the creation of the Johannesburg Stock Exchange in 1887, and major local political upheaval and change. This included the South African War (also known as the Anglo-Boer War, 1899 to 1902), two world wars, and institutionalised apartheid.
Every development accentuated the need for more accountants and auditors, recognised standards and training, a generally accepted exam system, and a register of qualified accountants. The first representative bodies were the Institute of Accountants and Auditors in the South African Republic (IAASAR) in 1894 and the South African Committee of the Society of Accountants (SAC) in the Cape in 1896. By 1910, when the Union of South Africa created a political union of the four separate geographical areas, each of the Transvaal, Orange Free State and the British colonies of the Cape and Natal had formed local accounting bodies.
Meanwhile, in 1909, the Transvaal Society of Accountants (TSA) published the first professional publication for accountants – the quarterly The South African Accountants’ Journal, which was renamed The South African Accountant and Auditor in 1911 and merged with The South African Accountant in 1917.
In 1921 the four local accounting societies agreed to establish the South African Accounting Societies’ General Examining Board (GEB) to enforce standards within the profession, and in the same year the Free State, Cape and Transvaal accounting societies agreed to join forces to pursue legal recognition by Parliament of a national accounting body. However, there was no easy route to reach this goal and it would only be decades later, in 1980, that SAICA was finally established.
Major international and local political milestones included the passing of the Companies Act by the then Union Parliament in 1926 and the Chartered Accountants Designation (Private Act) 13 of 1927 that allowed members of the four chartered accountancy provincial societies to use the title of Chartered Accountant (South Africa), or CA(SA). In the same year that World War II (1939 to 1945) ended, the four provincial societies and the Rhodesian Society of Accountants (RSA) created the influential Joint Council of the Chartered Societies of South Africa (JC). By 1950, the General Examining Board (GEB) allowed certain universities to teach accountancy and set exams. The promulgation of the Public Accountants’ and Auditors’ Bill 51 of 1951 to regulate the accountancy profession and provide for a single register of public accountants created the Public Accountants’ and Auditors’ Board (PAAB).
Meanwhile, formalised apartheid had arrived in 1948 when the government of Jan Smuts was replaced by the National Party under DF Malan. Apartheid legislation included, for instance, the Extension of University Education Act of 1960 that created separate institutions of higher education for white, black, coloured and Indian people.
The country was shaken by the events in Sharpeville in 1960 when 67 people were killed after public protest against the carrying of passes. A year later (1961) South Africa left the British Commonwealth to become a republic. Increasing political strife and economic isolation followed.
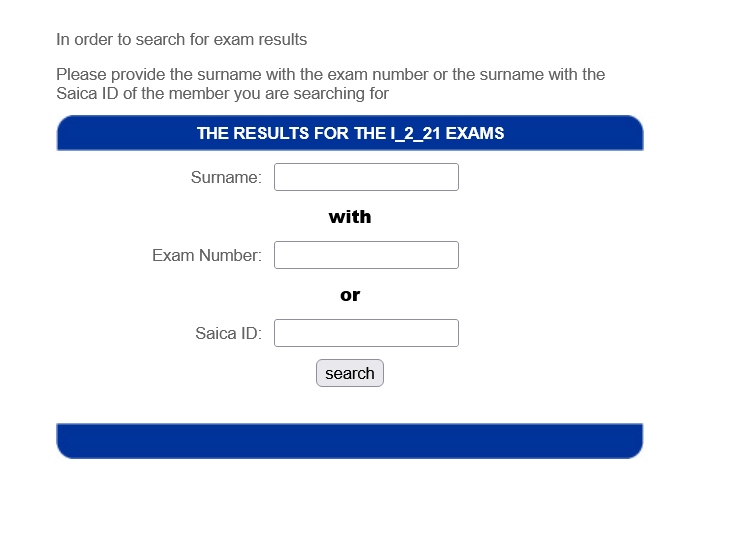
HOW TO CHECK SAIC ITC & APC RESULTS
The South African Institute of Chartered Accountants (SAICA)Exams Results Published on its Official website RESULTS Portal Here on this Article will Guide you to check and You’ll get Direct link to get your Results
👉Visit SAICA Official website
👉 Check on categories List
👉Find Results category click
👉Provide your login information
(as provided on Registration time)
=> Username
=>Exam Number
=>SAICA ID
What is ITC pass rate?
SAICA ITC AND APC PASS RATE
How many times can you write APC SAICA?
Qualify as a Chartered Accountant (SA)
Qualifying as a Chartered Accountant (SA) usually takes 7 years (3-year degree; 1-year honours and 3-years internship) provided you are able to complete the undergraduate qualification; postgraduate qualification and board exams in the minimum time. It is possible to qualify as a Chartered Accountant (SA) within 6 years by working and studying at the same time.
Your journey to qualifying as a Chartered Accountant (SA) works as follows:
Step 1: Obtain an undergraduate degree accredited by SAICA. Visit SAICA’s website (www.saica.co.za) for a complete list of accredited degrees offered by accredited universities. The minimum time to complete this qualification is three years.
Step 2: Obtain a postgraduate qualification accredited by SAICA. This qualification is either in the form of an honours degree or postgraduate diploma and is referred to as CTA (Certificate in the theory of accounting). Visit SAICA’s website (www.saica.co.za) for a complete list of accredited universities offering the postgraduate qualification. The minimum time to complete this qualification is one year.
Step 3: Enter into an internship at a SAICA accredited training office. The duration of the internship is:
- 3 years if you have an accredited undergraduate degree, CTA or accredited bridging programme by the time you start with your internship;
- 4 years if you have a non-accredited degree, national diploma in internal auditing, cost and management accounting or taxation or national higher diploma in internal auditing, cost and management accounting or taxation; or
- 5 years if you have a matriculation certificate or equivalent
The 4-year and 5-year programmes can be reduced by one year should you obtain your accredited undergraduate degree within the necessary timeframe.
Step 4: There are two board exams that need to be written in order to qualify as a Chartered Accountant (SA). The first exam is the Initial Test of Competency (ITC) and can be written at the beginning of the year following the year that you obtain your CTA qualification. There are two examination opportunities per year for the ITC (January and June of each year). A CTA is valid for three years which means you will have a maximum of six attempts at passing the ITC.
The second exam is the Assessment of Professional Competence (APC) and can only be written once you have passed the ITC exam; successfully passed the Professional Competence Development Programme provided by an accredited institution and completed at least 20 months of your internship. The Professional Competence Development Programme remains valid for three years. If you fail to pass the APC during the 3 years you will have to complete the Professional Competence Development Programme again. Unlike the ITC, the APC exam is written only once a year in November each year.
Step 5: You will be eligible to register as a Chartered Accountant (SA) once you have passed the APC exam and completed your internship.
SAICA CONTACT DETAILS
Contact Us
Contact centre operation hours: 08:15 to 16:30 Monday to Friday
Closed on weekends and public holidays
Local: 08610 SAICA (72422) or 011 621 6600
Please remember that queries can also be logged and tracked via the Member Portal.
| Region | Physical address | Postal address |
| Northern Region: Telephone: 0861 072 422 Email: [email protected] | 17 Fricker Road Illovo Sandton Johannesburg, 2196 | Private Bag X32, Northlands, 2116 |
| Central Region: Telephone: 27 51 444 3674 Email: [email protected] | PHG Building C/O Nelson Mandela Ave & Nobel Str Brandwag Bloemfontein | PO Box 12911 Brandhof Bloemfontein 9324 |
| Eastern Region: Telephone: 27 31 207 3290 or 27 31 207 3251 Email: [email protected] | 50 West Riding Row Second Floor Office 11/12 Sherwood 4091 | PO Box 1350 Wandsbeck 3631 |
| Southern Region: Telephone: 27 21 417 2660 Email: [email protected] | 1st Floor Convention Towers Cnr Hereengracht & Walter Sisulu Avenue Foreshore Cape Town 8001 | P O Box 4484 Cape Town 8000 |
| SAICA International: Bruce Freer CA(SA) Telephone: +44 (0)7397 611 113Sarah Varney Telephone: +44 (0)7855 412 911 Email: [email protected] |
https://ajiraforum.com/south-africa is Just 3rd part site for more info Kindly Visit SAICA Official Website 
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE




Be the first to comment