JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
Rural Settlement Grade 12 Geography Revision Notes
Rural Settlement Grade 12 Geography Revision Notes Welcome Ajiraforum.com/southafrica From this page you will Get Rural Settlement Grade 12 Geography Revision Notes.
What is Rural settlement in South Africa?
What characterises a rural settlement in South Africa are the following:
- Farmstead: A single farm and outbuildings
- Hamlet: A loose grouping of a few farmsteads
- Village: A denser grouping of many farmsteads
Rural settlements are the smallest settlements which are unifunctional. They are farmsteads, hamlets or villages, where primary activities (farming, fishing, forestry or mining) take place.
Land use in rural settlement in South Africa
The largest land use in South Africa is agriculture. Approximately 12, 1% of the land is used for both commercial and subsistence cultivation of crops.
Although rural communities focus on primary economic activities (farming and forestry), there are a number of different ways in which the land in these settlements can be used.
Subsistence farming involves using the land to grow crops and breed animals that are a source of food for the family living on the farm. The aim is not to sell the goods, but to consume them.
Commercial farming is practised where the land is used to grow crops or breed animals that are then sold as food sources to other markets. The main aim of this rural land use is to generate income for the farmers. Commercial farming can be either intensive or extensive. Commercial farming can be divided into:
- Stock farming: Animals, for example, cows, chicken, sheep, pigs.
- Crop farming: Cultivation of land, for example, maize, wheat, fruit, vegetables.
- Mixed farming: A combination of stock and crop farming.
Rural Settlement Grade 12 Geography Video Lesson
Rural Settlement Geography Grade 12 main questions and answers
Question: What is agenda 21 local examples in South Africa?
Answer:
- Including local communities in all decisions made.
- Using local resources wisely.
- Including indigenous knowledge.
- Developing the local community and improving the quality of life of people alongside conservation strategies.
Question: Give two examples of important break of bulk points
Answer:
Where one type of transport is replaced by another type, e.g:
- Harbour: docks where goods are transfer from boat to truck.
- Airport: the ramp of a airport where goods are unloaded from trucks into planes.
Question: What is Informal settlement in South Africa?
Answer: An informal or unplanned area that is occupied by people who do not have access to formal housing and who erect dwellings on open land, usually on the outskirts of a town. Buildings are made of cardboard, zinc, plastic or wood, or any available materials. It is also sometimes called a squatter camp or shanty town.
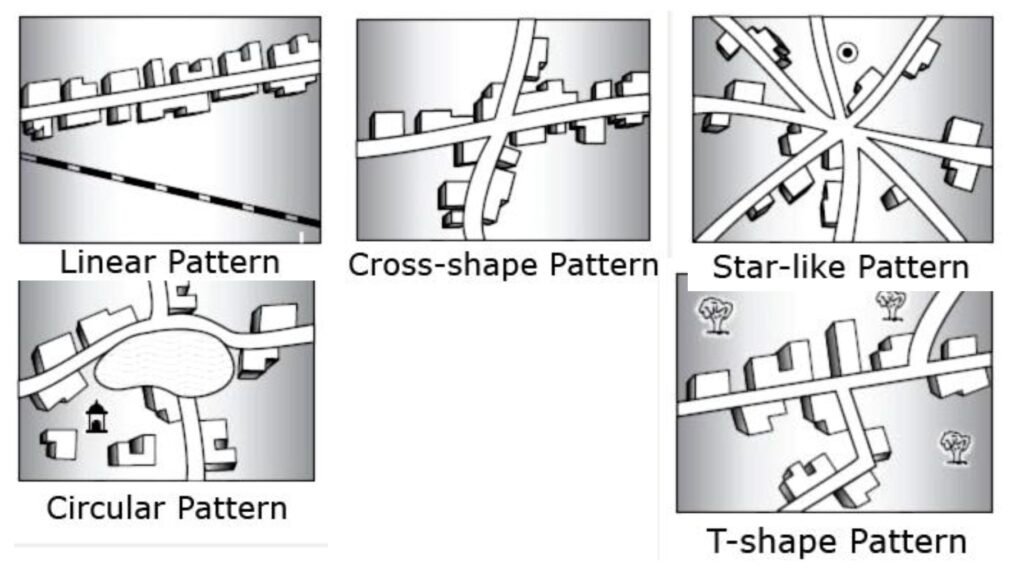
Question: List village shapes which are common in South Africa
Answer: Rural villages are classified as:
- Round – develop around a market place or some shared / communal land
- Linear – develops along rivers, roads, coastlines, railways or in thermal belts in valleys.
- Cross road – settlement develop in the form a cross to allow every one access to the road.
- T-shape – settlement develop in the form a T along a road junction to allow every one access to the road.
- Star-shaped – many roads connect and the settlement spread out along these toads.
How site and situation affects rural settlement in South Africa
Site of settlements are determined by the following:
- Running water for domestic and agricultural use
- Availability of building material e.g. wood, rocks, grass, mud, clay
- Flat land to build on
- Grazing land
- Fertile soil for crop farming
Downloadable Rural Settlement Grade 12 Geography Notes for Revision
Study Guides
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE

Be the first to comment