JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
Male reproductive system Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes with Activities Questions and Answers
Male reproductive system Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes with Activities Questions and Answers In order to help students in grade 12 get ready for their tests and examinations, this page contains revision exercises with questions and answers under the heading Male Reproductive System Grade 12 Life Sciences Notes.
Notes
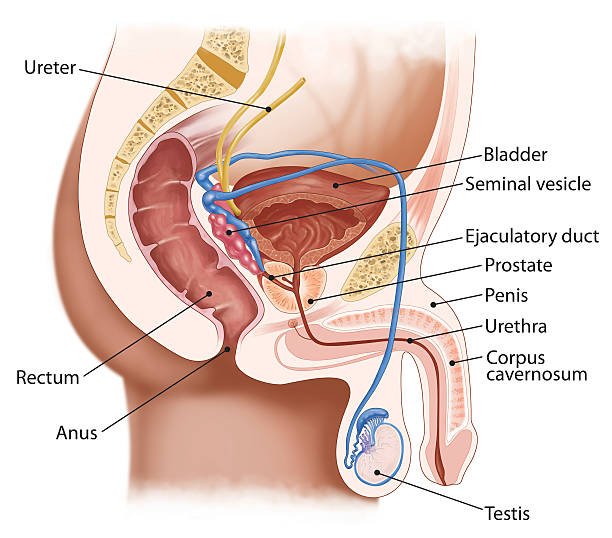
- Seminal vesicle: A gland that produces a nutrient- rich fluid that that provides energy for the sperm cells
- Cowper’s gland: Produces mucus that helps with the movement of sperm cells
- Scrotum: Skin sac that protects the testes and holds the testes ‘outside’ the body, at a temperature that is 2°C below 37°C. This is the best temperature for the production of sperm
- Prostate gland: Produces an alkaline fluid that neutralises the acids produced in the vagina, which would kill sperm cells
- Sperm duct: Transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra
- Urethra: Transports semen and urine out of the body
- Epididymis: Sperm cells mature and are stored here
- Testes: Produces sperm cells and the hormone testosterone
Functions of testosterone
The testes produce the hormone testosterone, which has the following functions:
- Development of male secondary sexual characteristics, such as beard, pubic hair, deep voice and a muscular body.
- Stimulates the maturation of sperm cells.
Structure of a sperm cell

- Acrosome: Contains enzymes to digest the wall of egg cell for fertilisation
- Nucleus: Contains 23 chromosomes
- Mitochondria: Provide energy for swimming
- Tail: Used for swimming
PDF Downloadable Notes on Male reproductive system:
Question and Answers Activities:
Find short and long questions for Grade 12 Life Sciences, which will help you to prepare for the exams, tests, practical tasks, and assignments.
Questions
- Name the accessory glands of the male reproductive system and give ONE function of each.
- Name the organ where testosterone is produced.
- Give TWO functions of testosterone.
- Name all the parts of the sperm cell that are responsible for movement. State what the function of each part is.
- Explain the role of the nucleus of the sperm cell in fertilisation.
Answers
- Seminal vesicle, produces a fluid that contains nutrients, for
the sperm cells, so that they have energy to swim.
Prostate gland, produces an alkaline fluid, that neutralises acids, produced in the vagina, so that sperm cells are protected, Cowper’s gland, produces mucus, that helps with the movement, of sperm cells. - Testes
- Testosterone is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, and it stimulates the maturation of sperm cells.
- Mitochondria, provide energy for swimming. Tail, moves in a whip-like fashion to propel the sperm cell forwards.
- The nucleus contains 23 chromosomes, and fuses with the nucleus of an egg cell, which also contains 23 chromosomes, The result is a zygote with
46 chromosomes 2n
How to Pass Life Sciences Grade 12 with distinctions
One of the most significant accomplishments in your academic career is passing matric. It provides access to a wide range of post secondary options and employment possibilities. Use our best study advice to complete your matriculation, and you’ll succeed with flying colors.
- Attend class
- Ask questions
- Make notes
- Study
- Practise
- Study groups
- Extra class
- Motivation
- Complete assessments
- Prepare for the Exams in due time
Download Past Exam Papers & Memo per Province
- Department of Basic Education Grade 9 Exams
- Eastern Cape Papers and Memorandum
- Free State Papers and Memorandum
- Gauteng Papers and Memorandum
- KwaZulu-Natal Papers and Memorandum
- Limpopo Papers and Memorandum
- Mpumalanga Papers and Memorandum
- Northern Cape Papers and Memorandum
- North West Papers and Memorandum
- Western Cape Papers and Memorandum
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE

Be the first to comment