JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
How to Calculate Magnetic Declination in Geography
How to Calculate Magnetic Declination in Geography Using the magnetic declination formula, one can determine magnetic declination in geography as follows: Let’s first clarify what magnetic declination is. Magnetic declination is the angle between true north and magnetic north. Magnetic variation is another name for magnetic declination.
The difference in degrees between True North and MAGNETIC North can also be used to understand magnetic declination.
See the below example on how to work out magnetic declination:
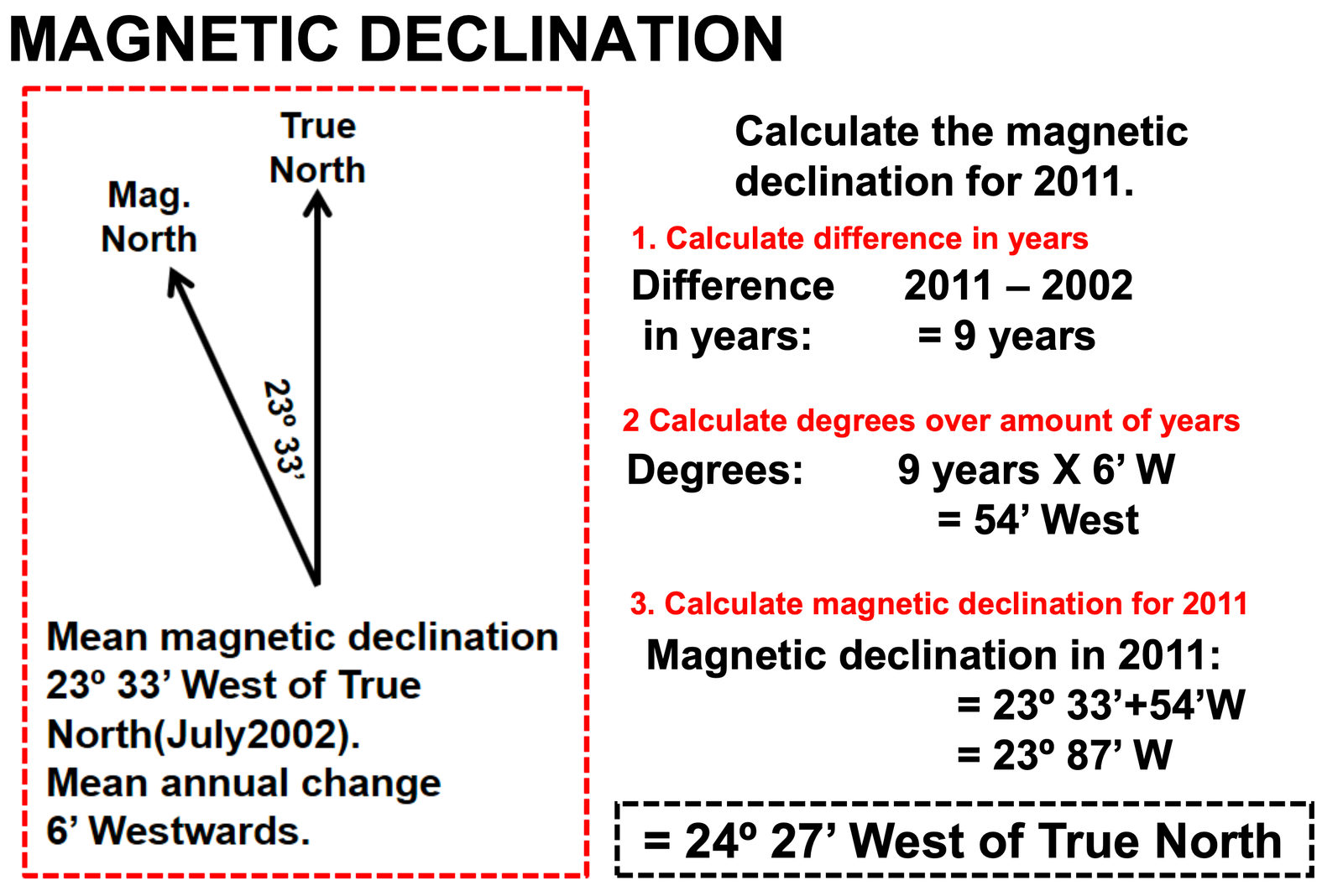
Did you know? By convention, declination is positive when magnetic north is east of true north, and negative when it is to the west. Isogonic lines are lines on the Earth’s surface along which the declination has the same constant value, and lines along which the declination is zero are called agonic lines. The lowercase Greek letter δ (delta) is frequently used as the symbol for magnetic declination.
Guide on how to Calculate Magnetic Declination in Geography
How to calculate magnetic bearing
Step 1: Determine the true bearing E.g 75°
Step 2: Determine the difference in years between the current year & the year
the Magnetic declination was measured (on topographic map). E.g. 2015 – 2005 = 10 years
Step 2: Calculate the total magnetic change
E.g 10 years x 2’ West = 20’ West (On the topographic map the change is 2’ West every year)
Step 3: Calculate the current magnetic declination
E.g 16°3’ West + 0°20’ West, When the mean annual change is west you add, & if the change is East, you subtract. = 16°23’ West Therefore, the magnetic declination for 2015 is 16°23’ west from True North.
Step 4: Calculate the magnetic bearing
E.g True Bearing + Current Magnetic Declination
= 75° + 16°23’
= 91°21’ west.
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE

Be the first to comment