JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
Geography Grade 12 Research Tasks (Topics) and Memos for: term 1, Term 2, Term 3 and Term 4
Geography Grade 12 Research Tasks (Topics) and Memos for: term 1, Term 2, Term 3 and Term 4 Utilizing a variety of assessment methods, assessment is a continual, organized process for locating, compiling, and analyzing data regarding student performance. It entails four steps: creating and gathering evidence of achievement; assessing this evidence; documenting the findings; and using this information to comprehend and support the development of the learners in order to enhance the learning and teaching process. Both informal (evaluation for learning) and formal assessments should be conducted (assessment of learning). In both situations, learners should receive regular feedback to improve the learning process.
School-based assessment (SBA) is a deliberate gathering of student work that narrates the tale of students’ attempts, development, or success in particular areas. The effectiveness of SBA tasks plays a crucial role in learners’ final test preparation.
This brochure provides schools and geography subject teachers with four sample SBA tasks. The teacher formally records SBA grades for certification and advancement needs. All students must complete the SBA component. Students who are unable to meet the conditions outlined by the policy may not be allowed to enter the subject in the final exam.
The formal evaluation activities give the teacher a methodical technique to gauge how well students are developing. There are tests, a project, and a case study in this article. A year-long formal program of assessment includes tasks for formal assessment. It is important to take these activities seriously and to urge students to submit their best work for evaluation.
The evaluation assignments should be appropriate for and relevant to the students being taught, according to the teachers’ expectations. The assignments should be context-bound and tailored to the students’ level of comprehension, but teachers must also be aware of the guidelines outlined in the Curriculum and Assessment Policy Statement (CAPS) document.
What Skills are Assessed for Research Tasks in Grade 12
The following skills are assessed. Some/All of these skills may be tested in any external examination:
- Gathering data
- Interpreting data
- Analysing data
- Comparing different sets of data
- Representing data in written, graphic or mapped format
- Problem-solving
- Drawing conclusions
- Hypothesis statements
Research framework for assessment (Guideline on administration of research task)
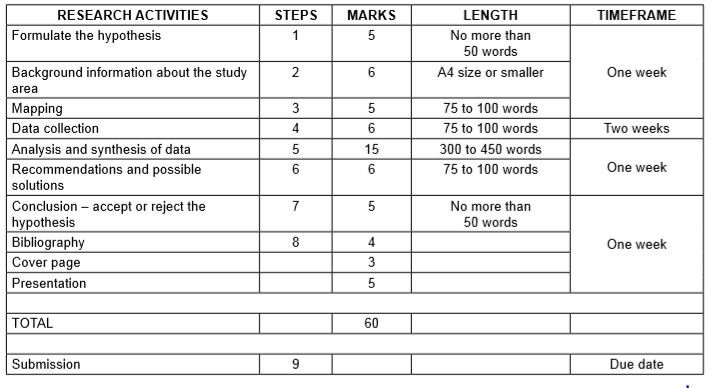
Step 1: Formulating a hypothesis/problem statement.
Guideline: Geography Grade 12 Research Tasks
Step 1: Formulating a hypothesis/problem statement. As Geographers we seek to understand and explain the interactions amongst humans, and between humans and the environment in space and time. This is achieved by asking questions or making informed geographical decisions. This entails the development of a hypothesis or a problem statement to be tested.
- You have to choose a specific area of study where a geographical problem exists.
- During this stage, a geographical question showing a problem is asked.
- Identify the problem from a local area.
- Formulate a hypothesis or a problem statement. (Hypothesis research is used to prove that certain variables are dependent on or independent of each other. Problem statement research is only to highlight that a specific problem exists in a specific community.)
- You should then follow the steps of research to ensure that the geographical question is answered.
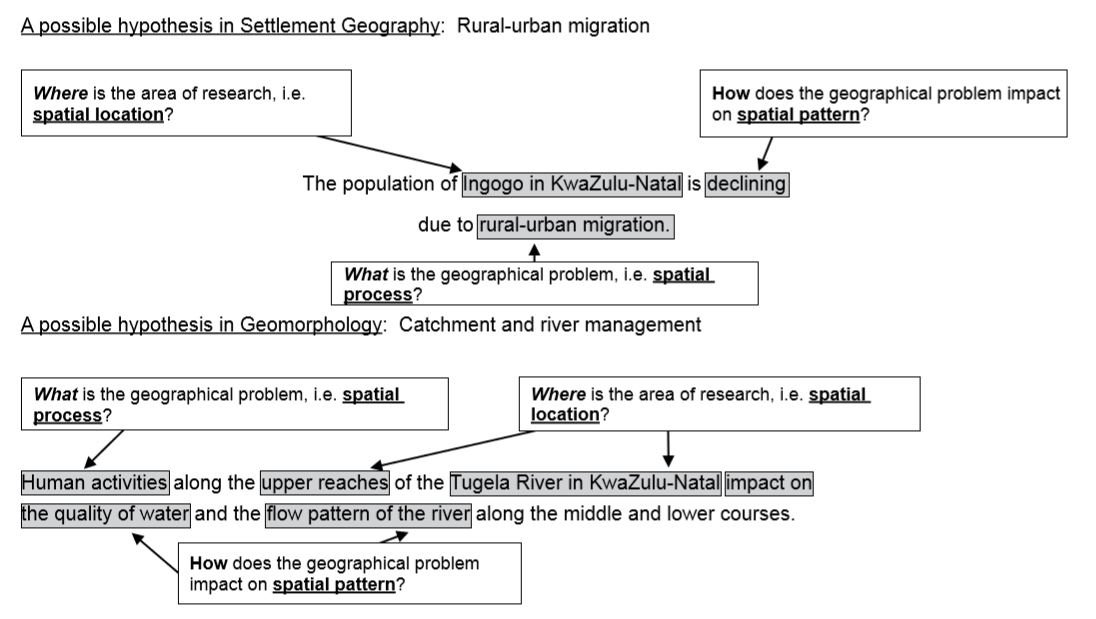
Geography Research Project Topics for Grade 12 South Africa
- The value of property along north-facing slopes is higher than the value of property along south-facing slopes in Meyersdal, Gauteng (choose local area).
- The cause of rural-urban migration in Ndwedwe, KwaZulu-Natal (choose local area), is the lack of service delivery in the health sector.
- Climate change will impact negatively on grape farming and related industries in the Western Cape.
- The closing down of many primary schools in Lusikisiki (Eastern Cape) (choose a local area) is due to a decline of the population in the age group 7 to 15 years.
- The poor condition of roads (specify the names of the roads) leading to/in Harrismith, Free State (choose local area), is due to the lack of proper planning by the local municipality.
- The impact of building a dam along the Jukskei River in Gauteng (choose local area) upstream of Alexandra will reduce flooding and the subsequent loss of life in Alexandra.
- The e-toll system will impact negatively on the economic position of people using private transport in Gauteng.
- The e-toll system will impact positively on traffic flow to the major urban centres in Gauteng.
- Informal settlements in the Vhembe district of Limpopo have low levels of development due to the lack of provision of basic needs (choose ONE informal settlement in your local area.)
- Overcrowding of informal settlements is due to the lack of proper planning by the local government (choose local area).
Step 2: Background information about an area of study
- You must explain where in South Africa the study area is located. (This can be indicated on the map.)
- Describe the study area in terms of its exact position (degrees, minutes and seconds).
- Provide relevant information about the area, for example population of the area or climate of the area.
Step 3: Mapping
- You must provide a map of the area in question.
- During this stage you must create a buffer zone around the area where the geographical problem exists.
- The map should have a clear legend/key and must be drawn to scale. The scale must be indicated on the map.
- If the map used covers a wider area, buffer zones around the area of study should be created.
- The map used should be the most recent map of the study area
Step 4: Methods of data collection
(a) PRIMARY DATA SOURCES
- The use of questionnaires
- Interviews
- Observations
- Field trips
(b) SECONDARY DATA SOURCES
- Newspaper articles
- Government department statistics
- Books
- Internet
Step 5: Analysis and synthesis of data
• Learners must use collected data now to formulate a discussion around the existing geographical problem. • At this stage learners should represent some of the information graphically where necessary, for example graphs and sketches. • Learners must analyse graphic information during this stage.
Step 6: Recommendations and possible solutions
• Learners should now make recommendations to solve the geographical problem in question. • Learners should present their original and realistic opinions as far as they possibly can.
Step 7: Conclusion – accept or reject the hypothesis
- Learners should now take a decision to either ACCEPT or REJECT the hypothesis.
- Learners must give reasons for either ACCEPTING or REJECTING the hypothesis
Step 8: Bibliography
- Learners must include a comprehensive bibliography.
- Learners must list websites in full.
- Learners must include annexures of questionnaires and interviews conducted
Geography-English-SBA-Caps-Teacher-Guide-1Download
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE

Be the first to comment