JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP. CLICK HERE
Mapwork Skills Notes for Geography Grade 12
Mapwork Skills Notes for Geography Grade 12 This website focuses on Mapwork Skills for Geography Grade 12 Students. You can obtain notes and directions in pdf format.
Let’s understand what Maps are
Maps show what the world looks like from above. They are very useful because they give information and show where places are. There are many different types of maps. These include street maps, road maps, atlases and ordnance survey (OS) maps.
Map Techniques you should know
- A map is a reduced representation of reality.
- Maps are either drawn on paper or produced digitally.
- Maps show reality in two dimensions. If we want to represent the third dimension (height or altitude) we have to use contour lines or spot heights.
- On many maps (including synoptic maps) it is not necessary to show altitude. However, symbols are needed to represent other information on the map.
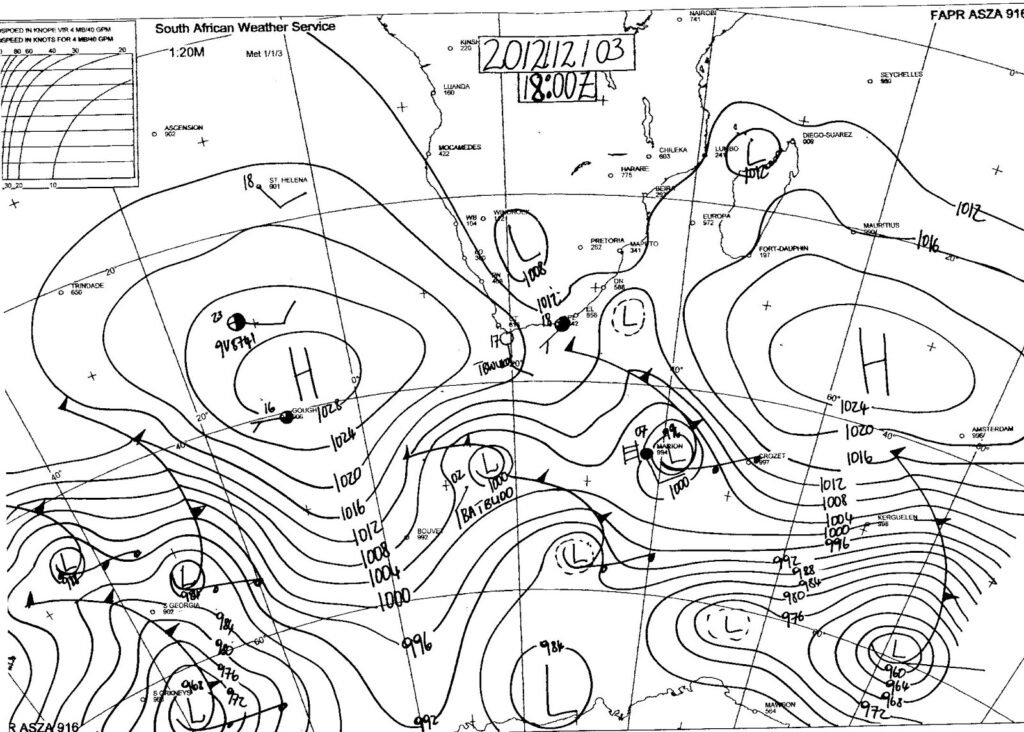
- A synoptic weather map provides a summary of weather conditions over a particular area at a particular time.
- Synoptic charts, satellite images and other data give us valuable information about the weather and climate.
- To make a weather forecast, forecasters examine a series of synoptic charts and compare them to satellite images and data from weather stations and weather balloons.
- Synoptic charts show weather-related data only and include isobars, station models (the symbols that show a variety of conditions) and weather features.
- Satellite images are remotely sensed. This means that there is no contact between the sensor in the satellite and the item being sensed (e.g. the Earth’s surface).
- Satellite images are digital images captured by sensors in satellites that orbit the Earth.
- Meteosat satellites are weather satellites and their sensors capture images of large areas.
- Satellite sensors don’t just capture images; data is also collected from outside the visible light spectrum, for instance, infrared.
Map and photo interpretation: reading and analysing features
- In settlement geography, map and photo interpretation is just as important as in physical geography.
- Settlements are often influenced by physical features (slope steepness, soil, availability of water, avoidance of marshy areas and wetlands), so you must be able to read and analyse physical features in the landscape.
- Constructed features are those things which humans place (build) on the landscape to serve their needs.
- Communications and transport (telephone lines, roads, railways), power lines, dams, and the settlements themselves are examples of constructed features.
Downloadable Guides and Notes for Mapwork Skills for Geography Grade 12
JOIN OUR TELEGRAM CHANNEL. CLICK HERE

Be the first to comment